Air Liquide and hydrogen production by water electrolysis
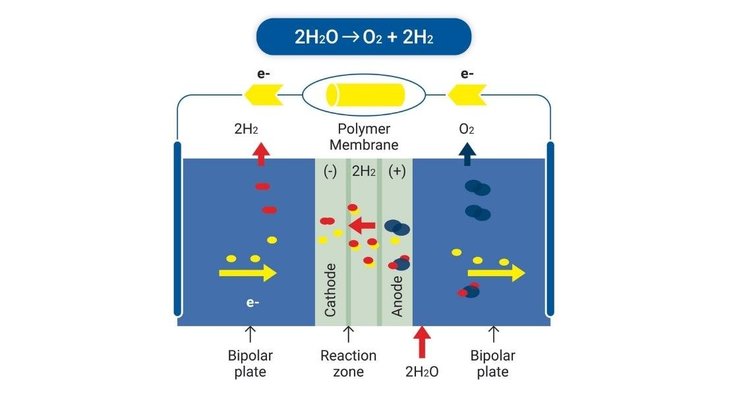
Electrolysis consists of splitting water molecules (H2O) by means of an electric current and thus obtaining hydrogen and oxygen.
Inaugurated in 2018, the 1.2 MW HyBalance electrolyzer in Hobro, Denmark, is one of the first European facilities to produce hydrogen by PEM electrolysis on an industrial scale. In January 2021, Air Liquide inaugurated the world's largest renewable hydrogen production unit by membrane electrolysis (20 MW) in Bécancour, Canada. The Air Liquide Normand'Hy project of at least 200 MW represents a strategic investment to support the large-scale production of renewable hydrogen in France.
What is electrolysis?
Electrolysis consists of splitting water molecules (H2O) by means of an electric current and thus obtaining hydrogen and oxygen.
This method does not emit carbon dioxide and allows the production of so-called "low carbon" hydrogen.
However, it is important to consider how the electricity is produced. If the electricity is generated from renewable sources (using wind turbines or solar panels, for example), then the hydrogen is produced without any greenhouse gas emissions and is said to be "renewable".
Siemens Energy and Air Liquide have joined forces to combine their expertise in electrolysis technology
Early 2021, Siemens Energy and Air Liquide have joined forces to combine their expertise in Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolysis technology for sustainable hydrogen production.
This cooperation is supported by the French and German governments with the aim of initiating a European ecosystem for electrolysis and hydrogen technologies. Large hydrogen projects for industrial scale deployment of large capacity electrolysers have already been identified. This is particularly true of the Air Liquide Normand'Hy project.